Sharia law is just about having people face consequences for their immoral and anti-social choices.
Hudud Punishments (Fixed Punishments for Specific Crimes)
- Theft: Amputation of the hand.
- Adultery (Zina): Death by stoning (for married persons) or 100 lashes (for unmarried).
- Apostasy (leaving Islam): Punishable by death in traditional interpretations.
- Blasphemy: In some countries, it can lead to execution or long prison terms.
Gender Inequality in Legal Matters
- A woman’s testimony is worth half that of a man in some legal contexts.
- Inheritance laws often grant sons twice the share of daughters.
- Men can unilaterally divorce their wives (talaq), while women often face more legal hurdles.
- Strict dress codes for women (e.g. compulsory hijab, niqab) are enforced by law.
Corporal Punishment for Drinking Alcohol or Fornication
- Flogging (e.g. 40–80 lashes) for consuming alcohol or premarital sex in certain countries like Saudi Arabia or Iran.
Restrictions on Non-Muslims
- In some interpretations, non-Muslims can't openly practice their religion or build new places of worship in Muslim-majority countries (e.g., Saudi Arabia).
- Payment of a special tax (jizya) by non-Muslims under a traditional Islamic governance system.
Freedom of Speech and Expression Limits
- Criticism of Islam, Muhammad, or even questioning Sharia law can be criminalized under blasphemy laws.
- Artistic, literary, or journalistic content seen as “un-Islamic” may be banned or punished.
LGBTQ+ Rights
- Homosexual acts are criminalized and can carry severe penalties, including the death penalty in some Sharia-based systems (e.g., Iran, parts of Nigeria).



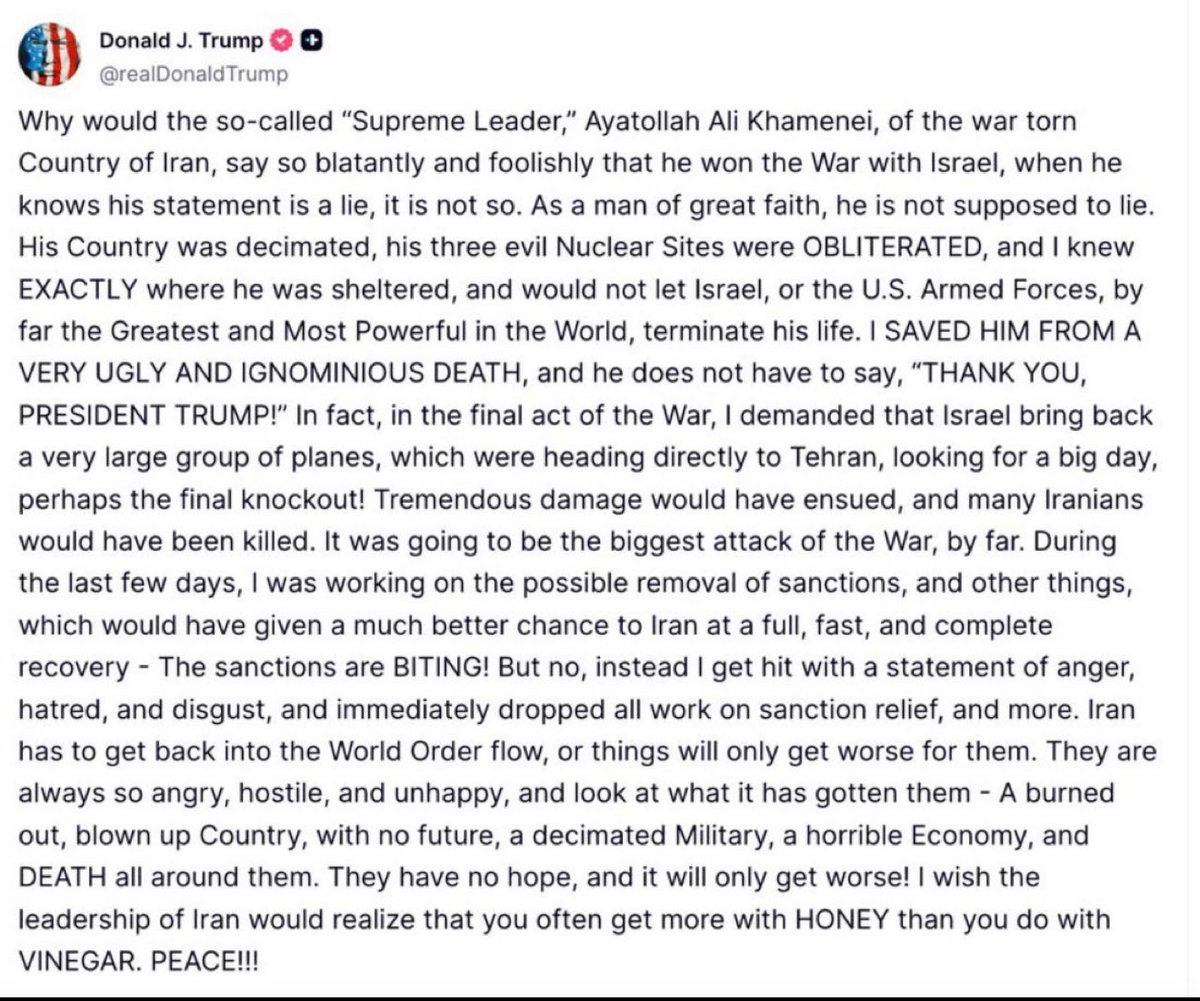

 White people i swear
White people i swear

